This article summarizes the difference between free and total chlorine.
Important Terms to Know
> Free chlorine: combination of Cl2, HOCl, and OCl-
> Combined chlorine: consists of mostly chloramines, which are formed when ammonia is added to free chlorine, yielding monochloramine (NH2Cl), dichloramine (NHCl2), trichloramine (NCl3), and organic chloramines
> Total chlorine: combination of free and combined chlorine in solution
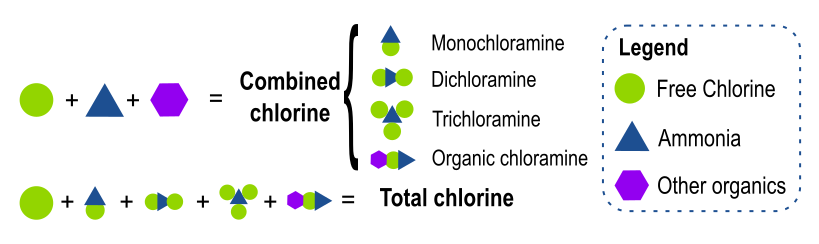
The above graphic illustrates the relationship between free, combined, and total chlorine. When free chlorine (shown by the green circle) is added to a solution containing ammonia and other organics, combined chlorine forms. Combined chlorine consists of monochloramine (NH2Cl), dichloramine (NHCl2), trichloramine (NCl3), and organic chloramines. Total chlorine encompasses all of the free chlorine and whatever forms of combined chlorine might be present.
What Makes The Measurements Different?
The main difference is which probe you will use. The Kuntze Zirkon® DIS sensor is for free chlorine measurement, and measures the presence of only hypochlorous acid (HOCl). The Kuntze Zirkon® DIS Total sensor measures the presence of all chlorine componenets which allows the analyzer to give a total chlorine measurement.
Important Things to Keep in Mind
> Be sure your reference measurement is configured to measure the correct parameter, and
that you have purchased the correct reagents to do so.
> The free chlorine measurement works best below pH 8.5, while the total chlorine
measurement is capable of going up to pH 10.
> If you have any further questions, please contact a Kuntze representative.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.